Inflation is a critical economic indicator that reflects the health and stability of an economy. As the cost of goods and services rises, inflation directly affects the purchasing power of consumers and the overall economic well-being of a country.
Understanding the inflationary trends during the presidencies of Joe Biden and Donald Trump offers insight into the broader economic policies, external factors, and their consequences for everyday households.
This article provides an in-depth comparative analysis of inflation under these two administrations, focusing on key factors like economic policies, geopolitical events, and the impact on the U.S. economy and households.
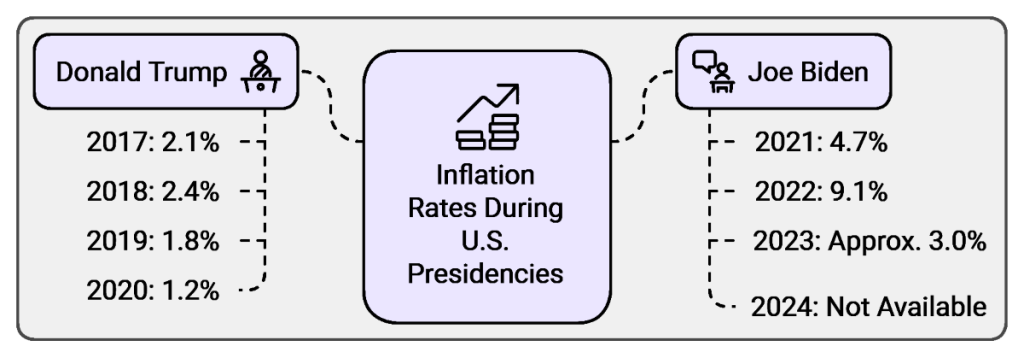
| Year of Presidency | Year | Donald Trump Inflation Rate (%) | Year | Joe Biden Inflation Rate (%) |
| 1st Year | 2017 | 2.1 | 2021 | 4.7 |
| 2nd Year | 2018 | 2.4 | 2022 | 9.1 |
| 3rd Year | 2019 | 1.8 | 2023 | Approx. 3.0 |
| 4th Year | 2020 | 1.2 | 2024 | Not Available |
Introduction to Inflation
Inflation measures the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises over a given period. It’s often expressed as an annual percentage increase and is primarily measured using the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which tracks the price changes of a basket of consumer goods and services.
Moderate inflation is typically a sign of a growing economy, but when inflation becomes excessive, it erodes purchasing power and can destabilize economic systems.
The presidencies of Donald Trump and Joe Biden have faced different economic challenges, resulting in varied inflationary outcomes. Their respective policy decisions and responses to external events like the COVID-19 pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine conflict have shaped the inflationary landscape of the U.S. economy.
Inflation During Donald Trump’s Presidency (January 2017 – January 2021)

1. Initial Economic Conditions
Donald Trump assumed office in January 2017 when the U.S. economy was relatively stable. Unemployment rates were low, GDP growth was steady, and inflation was moderate. Throughout his first three years in office, inflation remained within a manageable range, with the CPI increasing by approximately 8% during his four-year term.
2. Key Economic Policies and Their Effects on Inflation
Trump’s economic agenda focused heavily on tax cuts and deregulation aimed at stimulating business investment and economic growth. One of the signature legislative achievements of his administration was the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017, which reduced corporate and individual tax rates. The administration also emphasized energy independence, promoting the expansion of domestic oil and gas production, which helped stabilize energy prices.
While these policies spurred economic growth, their impact on inflation was relatively muted in the short term. The CPI grew moderately, with inflation rates ranging between 1.2% and 2.4% annually from 2017 to 2020.
3. The Impact of COVID-19 on Inflation
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020 brought about a dramatic shift in the U.S. economy. With widespread lockdowns, business closures, and disruptions to supply chains, demand for many goods and services plummeted, creating a temporary deflationary environment. In 2020, inflation rates were among the lowest of Trump’s presidency, hovering around 1.2%.
Although Trump’s administration implemented significant economic stimulus measures, such as the CARES Act, to combat the economic fallout of the pandemic, inflationary pressures remained subdued throughout 2020. The primary economic focus during this period was on stabilizing markets and supporting households and businesses rather than addressing inflation.
Inflation During Joe Biden’s Presidency (January 2021 – Present)

1. Post-Pandemic Economic Recovery and Rising Inflation
Joe Biden entered office in January 2021 amid a recovering economy. As the U.S. emerged from the pandemic-induced recession, inflationary pressures began to mount rapidly. Pent-up consumer demand, coupled with supply chain disruptions, labor shortages, and increased government spending, contributed to significant price increases across various sectors.
Year-over-year inflation surged during Biden’s first year in office, reaching a peak of 9.1% in June 2022—the highest rate in over 40 years. This spike in inflation has been attributed to a combination of factors, including:
- Increased consumer spending fueled by government stimulus payments.
- Supply chain disruptions caused by the global pandemic.
- Labor market shortages in key industries.
- Rising energy prices, exacerbated by geopolitical events, including the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
By August 2024, cumulative inflation since the beginning of Biden’s term had reached approximately 20%, significantly impacting the cost of living for American households.
2. Biden’s Economic Policies and Inflation
The Biden administration’s response to the pandemic included substantial federal spending to support economic recovery. One of the key initiatives was the American Rescue Plan, which provided direct payments to individuals, expanded unemployment benefits, and offered assistance to businesses. While these measures helped accelerate the recovery, they also contributed to rising inflation by boosting consumer demand.
In addition to stimulus measures, Biden’s administration has prioritized significant infrastructure investments through initiatives like the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. Although these investments aim to enhance long-term economic growth, some critics argue that the increased government spending has fueled inflationary pressures.
Moreover, Biden’s administration has also enacted regulatory measures, particularly in the energy and healthcare sectors, which have led to supply chain challenges and increased costs for businesses. Critics contend that these policies have added to the inflationary environment, particularly in sectors like energy, where prices have been volatile.
Key Factors Influencing Inflation Under Both Administrations
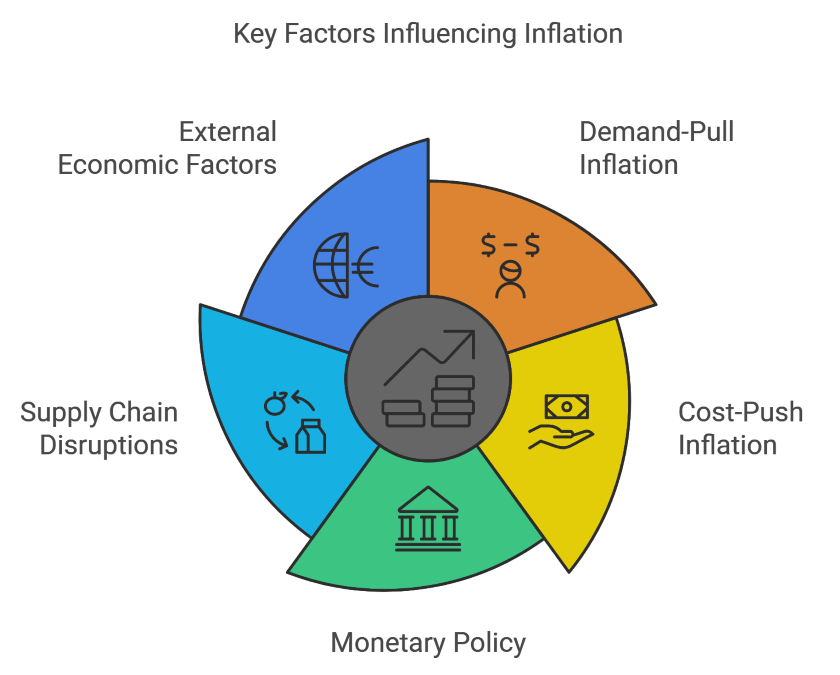
Several external and internal factors have played critical roles in shaping inflation during the Trump and Biden presidencies. These include:
1. Economic Policies
Trump’s Economic Policies: Focused on deregulation, corporate tax cuts, and energy independence. These policies supported economic growth without triggering significant inflation, particularly during the first three years of his presidency. The administration’s efforts to expand domestic energy production helped stabilize energy prices, mitigating inflationary pressures in this sector.
Biden’s Economic Policies: Characterized by increased government spending, regulatory actions, and significant federal investment in infrastructure. While these policies have aimed to promote economic recovery and modernization, they have also been linked to rising inflation. Increased government spending, particularly through stimulus packages, has been a major contributor to demand-driven inflation, while supply chain bottlenecks exacerbated by regulations have added to cost pressures.
2. External Events
COVID-19 Pandemic: Both administrations faced the economic challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. For Trump, the pandemic’s early impact led to a deflationary environment as consumer demand dropped sharply. Conversely, Biden’s administration dealt with the inflationary effects of a rapid post-pandemic recovery, where demand outstripped supply.
Geopolitical Tensions: The global impact of the Russia-Ukraine war, which began in early 2022, has significantly influenced inflation during Biden’s term. The war has led to disruptions in energy markets, particularly in Europe, but has also caused global oil and gas prices to rise, contributing to inflationary pressures in the U.S. The conflict exacerbated existing supply chain issues, driving up the cost of energy and other essential commodities.
3. Household Impact
The effects of inflation under both administrations have been felt acutely by households across the U.S. Here’s a look at how inflation influenced household finances during the Trump and Biden presidencies:
Trump’s Presidency: Under Trump, inflation remained relatively low, and the cost of living rose modestly. During his first three years, wages grew at a faster pace than inflation, leading to real wage gains for many workers. By the end of Trump’s presidency, however, the pandemic had caused economic disruption, but inflationary pressures remained contained, with household costs increasing at a slower rate.
Biden’s Presidency: The surge in inflation during Biden’s term has significantly impacted household budgets. Since January 2021, inflation has cost the average American household approximately $29,000, as prices for essential goods and services, including housing, energy, and food, have risen dramatically. While wages have increased by around 17.7% during this period, they have not kept pace with inflation, resulting in a net loss in purchasing power for many workers.
Comparative Economic Growth and Inflation
While inflation is a key economic indicator, it is also essential to consider how the overall economy performed under each administration. Economic growth, as measured by Gross Domestic Product (GDP), offers insight into the broader economic environment during each presidency.
1. GDP Growth Under Donald Trump
Trump’s economic policies, particularly the tax cuts and deregulatory measures, contributed to solid GDP growth during the first three years of his presidency. From 2017 to 2019, the economy grew at an average annualized rate of 2.7%. However, the pandemic’s economic toll in 2020 caused GDP to contract by 3.4%, marking the steepest decline in economic output since World War II.
2. GDP Growth Under Joe Biden
Biden’s presidency has seen strong post-pandemic recovery in terms of GDP growth, especially in 2021, when the economy expanded by 5.9%, driven by increased consumer spending and government stimulus. However, as inflationary pressures intensified and monetary policy tightened in response, economic growth has slowed, with annualized growth rates of around 2.5% in 2023 and 2024.
Inflation and Wage Growth Comparison
A critical aspect of inflation is how it interacts with wage growth, determining whether workers experience real gains in purchasing power or fall behind due to rising prices.
Trump Administration: During Trump’s presidency, wages grew by about 15%, outpacing inflation for most of his term. This led to real wage gains, improving the standard of living for many workers. By the end of Trump’s presidency, inflation remained low, and most households had seen their purchasing power increase.
Biden Administration: While wages have increased by 17.7% under Biden, they have not kept pace with the cumulative inflation rate of 20%. As a result, many workers have experienced a decline in real wages, leading to diminished purchasing power. This wage-inflation gap has been a significant source of economic frustration for many households, particularly those in lower-income brackets.
Conclusion: A Tale of Two Economic Strategies
The presidencies of Donald Trump and Joe Biden present stark contrasts in terms of inflationary trends and the broader economic strategies used to manage the U.S. economy.
Donald Trump’s Presidency: Characterized by low inflation and stable economic growth, Trump’s administration prioritized tax cuts, deregulation, and energy independence, which helped maintain price stability until the pandemic’s arrival. While the pandemic caused significant economic disruption, Trump’s policies helped keep inflation under control for most of his term.
Joe Biden’s Presidency: Defined by rapid inflation and post-pandemic economic recovery, Biden’s administration has faced unprecedented challenges in managing inflation, which reached its highest levels in decades. The administration’s policies, including substantial government spending and infrastructure investments, have contributed to inflationary pressures. External factors, such as the Russia-Ukraine conflict, have further complicated efforts to stabilize prices.
Both administrations have faced unique economic challenges, but inflationary outcomes have varied dramatically due to their differing policy approaches and external events. As the U.S. continues to grapple with inflation and other economic challenges, understanding these dynamics is essential for evaluating current conditions and predicting future trends.
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics





